Blood Establishment Computer System
At SCC Soft Computer, we offer a cutting-edge suite of solutions designed to streamline workflows, enhance productivity, and drive breakthroughs in patient care. Our mission is to revolutionize the way laboratories operate, whether you’re part of a health system, regional hospital, public health service, commercial lab, research facility, blood management organization, or transplant medicine unit.
Enterprise Scale
- Customized modules and product suites designed to meet the unique needs of enterprise laboratories.
- Seamless integration with existing enterprise systems to streamline workflows and enhance interoperability.
- Industry-leading security measures to safeguard sensitive laboratory data and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Dedicated technical support and comprehensive training programs.
Commercial Flexibility
- Flexible modular solutions that cater to the specific needs and budget constraints of smaller labs.
- Scalable cloud-based solutions that enable growth without significant upfront investment in infrastructure.
- Custom workflow engine to automate processes to improve operational efficiency.
- Full suite of outreach and operational solutions to improve customer service and revenue cycle management.
Driving Growth Across Diverse Industries
SCC Soft Computer is dedicated to delivering tailored solutions that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and excellence for clients across a wide range of industries, from complete healthcare systems to commercial labs.
Health Systems
Our solutions help health systems streamline workflows and improve the coordination of patient care, especially in facilities with multiple sites. By unifying systems under a single database, SCC products reduce turnaround times and facilitate seamless operation across different time zones, eliminating the need for multiple systems.
Solutions for Health Systems ›
Regional Hospitals
For regional hospitals, SCC solutions optimize resource utilization and elevate the quality of patient care. Our consistent interface design ensures a smooth user experience, while direct integration with laboratory instruments eliminates the need for middleware, simplifying operations and reducing errors.
Solutions for Regional Hospitals ›
Research
Research laboratories benefit from our solutions through enhanced data sharing and collaboration capabilities, crucial for high-volume testing environments. Our platforms perform real-time data analytics, enabling on-demand research and providing valuable insights that drive scientific discovery.
Solutions for Research ›
Commercial Laboratories
Commercial laboratories can achieve greater accuracy and efficiency in high-volume testing with SCC’s comprehensive solutions. Our LIS streamlines quality control workflows and minimizes the need for human intervention, allowing staff to focus on more critical tasks. Our integrated approach covers both the healthcare and business sides of operations, including revenue cycle management (RCM) for comprehensive operational oversight.
Solutions for Commercial Laboratories ›
Transplant Medicine
SCC Soft Computer’s solutions for Transplant Medicine provide unparalleled accuracy and efficiency, streamlining donor and recipient matching processes to ensure optimal outcomes. Our comprehensive software suite supports the entire transplant workflow, from data management and compliance tracking to real-time analytics, empowering healthcare professionals to deliver life-saving treatments with confidence.
Solutions for Transplant Medicine ›
Public Health
SCC Soft Computer’s solutions for Public Health Laboratories are designed to enhance disease surveillance, streamline testing workflows, and improve data management, ensuring timely and accurate reporting. Our robust software suite empowers public health professionals with advanced analytics and real-time monitoring capabilities, enabling them to respond swiftly and effectively to public health challenges.
Solutions for Public Health ›
Blood Management
SCC Soft Computer’s Blood Management solutions streamline the entire blood supply chain, from donor recruitment to transfusion tracking, ensuring the highest standards of safety and efficiency. Our advanced software suite offers seamless integration with laboratory systems, providing real-time data and analytics to optimize inventory management and enhance patient care.
Solutions for Blood Management ›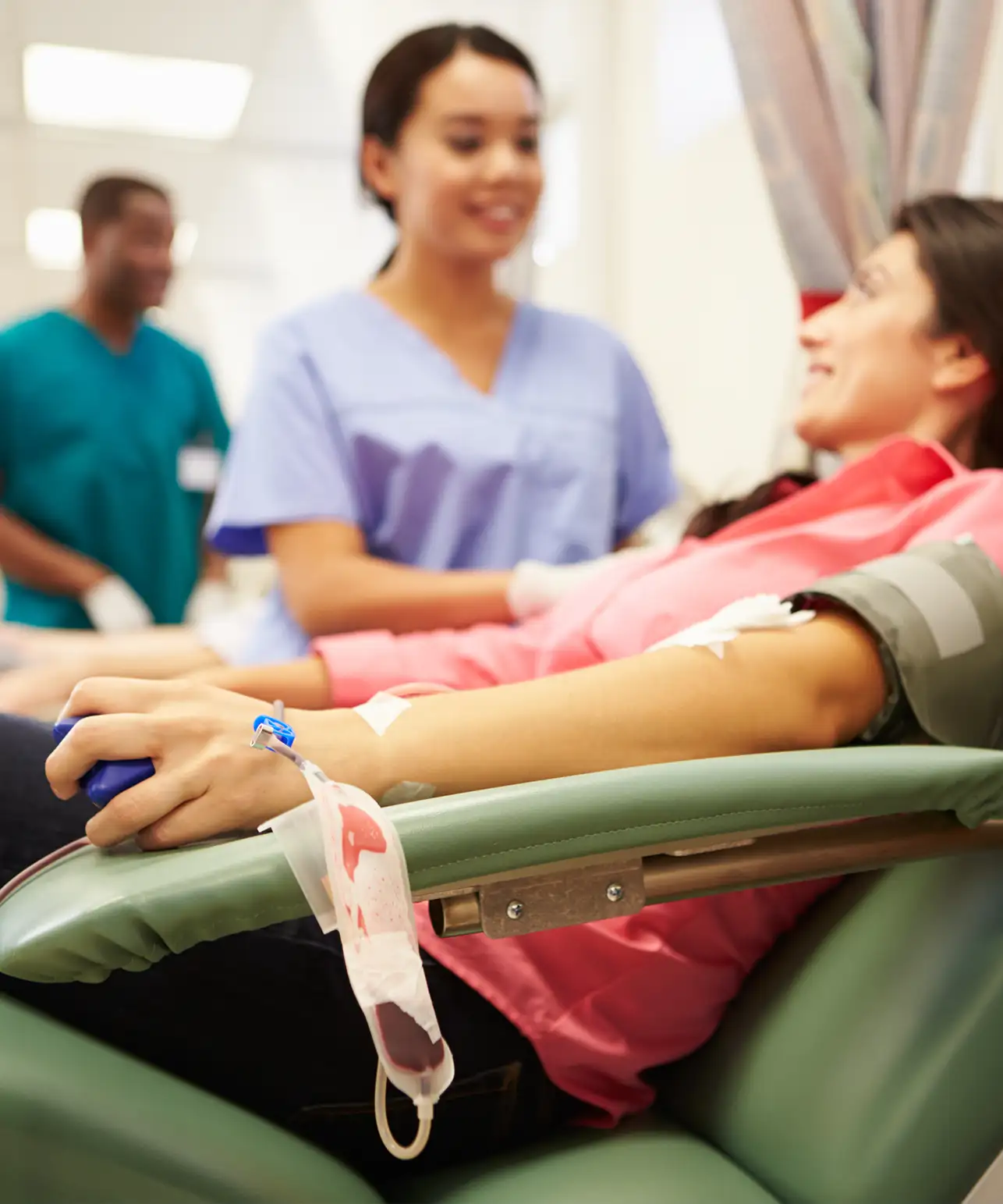
About SCC Soft Computer
Founded in 1979 by visionary leader Gilbert Hakim, SCC Soft Computer has established itself as a global pioneer in clinical information management systems. We specialize in providing state-of-the-art laboratory information systems (LIS) that empower healthcare organizations to optimize workflows, enhance patient care, and drive innovation. With a steadfast commitment to excellence, integrity, and customer focus, SCC Soft Computer combines cutting-edge technology with unparalleled support to deliver transformative solutions across diverse healthcare sectors. Our mission is to revolutionize healthcare by enabling laboratories worldwide to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and accuracy, ensuring that our clients remain at the forefront of medical advancements.
About UsBlood Establishment Computer System
SCC Soft Computer designs blood establishment computer systems to standardize transfusion services, improve traceability, and reduce error-prone manual steps across donor and patient workflows. A modern BECS ties instrument interfaces, electronic orders, inventory management, and bedside verification into one environment for teams to maintain control under regulatory scrutiny. It also integrates with the laboratory information system and outreach portals to preserve a single source of truth for orders, results, labels, and audit trails.
A BECS must support patient safety at the point of care and during every handoff before and after. Positive identification at the bedside, logic-driven interpretation for crossmatch, antibody workups, and controlled labeling are table stakes. The system should also manage component production, modification, and distribution with a detailed chain-of-custody that tracks each component from creation to final transfusion or disposal. Inventory must capture units, derivatives, aliquots, and cellular therapy products, with utilization and wastage reporting aligned to quality programs.
SCC Soft Computer, SoftBank®, delivers this foundation. SCC’s blood bank and transfusion service information management system supports multisite operations on a single database, offers instrument connectivity without middleware, and streamlines EHR interfacing through an enterprise service bus. It also provides supervisor reviews, audit trails, daily traces, and trauma-focused workflows that multiple users can act on a single patient while preserving control.
Blood centers and hospital transfusion services need rigorous donor operations. That work depends on blood donor management software integrated with the BECS, covering donor eligibility, collection visits, component processing, testing, and distribution. SCC’s donor and recruitment applications connect to SoftBank to create a continuous, auditable workflow from first contact through delivery.
A BECS cannot live apart from the broader clinical ecosystem. It must map to regulatory frameworks and industry standards that govern identity, data integrity, and security. The baseline in the United States includes CLIA certification for clinical operations, CAP accreditation for quality systems, HIPAA privacy and security safeguards, FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records and signatures, and interoperability standards such as HL7 for health data exchange.

FDA-Approved Blood Bank Computer Systems
Clinicians ask for “FDA-approved” blood bank systems because they want assurance of safety and control. The practical reality is that BECS vendors build to FDA requirements while maintaining clinical quality frameworks such as CLIA and CAP to deliver a complete safety posture. The system must also handle electronic records with controls consistent with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for auditability, signatures, and tamper evidence. Refer to FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for the electronic records and signatures framework that applies to validated BECS environments.
Hospitals and independent blood centers expect an operational blood bank LIS that integrates with instruments and the EHR without brittle middleware. SoftBank® addresses these demands by connecting directly to blood bank analyzers and devices, increasing security while reducing intermediary points of failure. Its enterprise service bus simplifies connections with clinical systems, ensuring orders, results, and product assignments flow reliably.
SoftBank’s multisite capability keeps orders and product inventory synchronized across facilities using a single, centralized database. This approach enables centralized transfusion testing while allowing each site to keep local inventory authority, which helps large systems consolidate expertise without losing operational autonomy. During trauma response, SoftBank lets multiple users perform tasks on the same patient in parallel, combining unit selection and issuing to move products quickly and safely.
Inventory control spans more than blood components. Transfusion services increasingly manage cellular therapies, human milk, and derivatives that require the same chain-of-custody, traceability, and reporting discipline. SoftBank tracks these products from receipt through final disposition and produces online utilization, inventory, and product history reports to support quality, billing, and compliance reviews. Component labeling follows ISBT conventions with print and verification controls, including routing labels to third-party services when required.
Quality oversight depends on timely reviews, exception handling, and evidence that processes occurred as intended. SoftBank generates management reports for daily quality activities, including test results, QC measures, exception reports, and audit logs that document changes. Supervisors can review performance across facilities without exporting data, which keeps the compliance footprint smaller and inspection readiness higher.
SCC’s BECS strategy also recognizes that donor engagement and bedside verification complete the safety envelope. SoftDonor.web™ manages donor eligibility, component production, testing, and distribution in alignment with transfusion service needs. SoftID.Tx® captures transfusion-related data at the bedside, assigns products to couriers, and verifies that the product issued matches the intended patient. Organizations reduce handoffs and paper, while tightening traceability from donor to recipient.
When evaluating any vendor’s claims, rely on published conformance to Part 11 controls for electronic records and signatures, along with demonstrable integration to standards, HL7 for order and result exchange. The combination of FDA expectations, CLIA operations, CAP quality systems, and standards-based interoperability defines a secure operating environment. HL7 provides the canonical message structures that BECS and LIS products should use for durable integration.
Finally, tie the regulatory conversation back to the system’s everyday usefulness. A compliant BECS that fails to keep pace with clinical workflows increases risk through workarounds. SoftBank’s design focuses on dependable instrument connectivity, streamlined EHR interfaces, multisite control, and trauma-ready workflows, which together reduce the need for ad hoc fixes.
Blood Bank Validation Protocol
Treat BECS validation as a lifecycle discipline, not a one-time event. Begin with a risk-based validation plan that maps system functions to clinical hazards and regulatory expectations. The plan should define test cases across specimen workflows, crossmatch logic, antibody investigation, product selection, issuing, returns, and adverse event documentation. Include instrument interfaces, EHR messaging, label controls, and audit trails. Cover role-based permissions, electronic signatures, date/time stamps, timeouts, and error handling.
Document a traceability matrix mapping requirement to test cases, expected outcomes, and evidence. Use sample patients representing complex histories, neonatal use cases, trauma scenarios, and multisite ordering. Evaluate online patient history retrieval through the master patient index and confirm that cross-facility encounters do not split histories. Validate instrument interfaces by simulating connectivity failures, delayed result postings, and duplicate transmissions to confirm idempotency and reconciliation.
Align the protocol to blood bank software regulations that apply to your operation. In the United States, the combination of CLIA certification for laboratory operations, CAP accreditation for quality systems, HIPAA privacy and security, and FDA regulation for electronic records and signatures through 21 CFR Part 11 forms the backbone for BECS validation. Build objective evidence around each of these pillars. Link your validation sections to the relevant references so auditors can quickly confirm scope.
Exercise trauma workflows where multiple users act on a single patient’s record concurrently. Confirm that unit selection and issuing combine safely while preserving audit trails and preventing double assignment. Validate neonatal functionality, including mother-newborn linking by MRN and policy controls for specimen validity horizons. Ensure component labeling adheres to ISBT standards, including label printing, verification, and any third-party routing from within the application.
Inventory validation must demonstrate end-to-end tracking for blood, derivatives, cellular therapy, and human milk from receipt through final disposition. Produce test evidence for product quarantine, release, wastage, and returns to stock. Include supply tracking for transfusion-related materials, with documentation that returned or unused items re-enter inventory only under controlled rules. Validate utilization, history, and exception reporting for quality review.
Demonstrate interoperability by transacting orders and results using HL7 messages. Verify the enterprise service bus routes messages, preserves acknowledgments, and records failures with retriable states. Confirm the integrity of electronic signatures, time-stamped audit entries, and change logs in compliance with FDA Part 11. Reference and retain the standard documentation for auditors: interface specifications, HL7 message examples, and signature policy statements.
Close validation with user training records, access provisioning reviews, and operational runbooks. Maintain a change control process that routes updates through regression testing and controlled release. For accreditation and internal quality, tie your completed package to CAP and CLIA documentation, recognizing that internal and external certification programs expect the same disciplined approach to traceability, data integrity, and record retention.
BECS Software
Teams evaluating BECS platforms should benchmark capabilities against the common features of BECS you rely on every shift. Start with direct instrument integration for analyzers and devices used in transfusion services. Reduce middleware when the BECS can connect natively, improving security and lowering points of failure. Expect dependable EHR interfacing through an enterprise service bus that supports reliable order entry, result reporting, and clinical acknowledgments.
Multisite control is another baseline requirement. Centralize testing and keep local inventory authority without fragmenting patient records. This lets you consolidate expertise while meeting service level goals across facilities.
Usability should extend beyond screens. Look for logic-driven workflows that guide interpretation, batch processing through online worksheets, and concise displays that improve decision speed.
Quality and reporting are non-negotiable must-have features. Expect daily QC, exception lists, audit trails, and supervisor reviews that span all sites. Management reports must support inspection readiness without exporting data.
Inventory and labeling breadth matter more each year. Your system should track blood, derivatives, cellular therapy, and human milk to final disposition, with ISBT-compliant labeling and verification. It should also document supply usage for component modification and safely return unused products to stock under controls.
Finally, validate edge-case workflows that stress the system. Trauma and emergency conditions demand concurrency and predictable issuing. Neonatal workflows require mother-newborn linkage, rule-governed specimen validity, and controlled product selection.
Choosing the Right Blood Donor Management Software
Selecting the best blood donor management software starts with scope. Do not treat donor operations as a standalone function. Donor eligibility, visits, component processing, testing, and distribution must feed your BECS and LIS without gaps. That requires a platform that manages donor-specific workflows while synchronizing component inventories and results with transfusion services.
SCC addresses donor operations with SoftDonor.web™, which helps teams manage eligibility, component production, donor testing, inventory control, and distribution in daily donor facility tasks. Because it is designed to work with SoftBank, it reduces reconciliation and preserves end-to-end traceability from donor through transfusion. Pairing SoftDonor.web with SoftBank and SoftID.Tx® closes the loop from recruitment to bedside verification.










